If you’re interested in learning about the inner workings of your vehicle, understanding the exhaust system is a great place to start.
The exhaust system is responsible for removing harmful gases produced by the engine and reducing noise levels.
It’s a crucial component of your vehicle’s performance and should be maintained regularly to ensure optimal function.
The exhaust system is made up of several parts, each with their own unique function.
The exhaust manifold collects exhaust gases from the engine and routes them to the catalytic converter, where harmful pollutants are converted into less harmful emissions.
From there, the exhaust gases travel through the muffler, where noise levels are reduced, and out the tailpipe.
Understanding the function of each part of the exhaust system can help you identify potential issues and make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs.
Overview of the Exhaust System
The exhaust system is an essential part of your vehicle’s engine, responsible for removing harmful gases produced during combustion.
It comprises several components that work together to ensure the safe and efficient expulsion of exhaust gases from your engine.
Purpose of the Exhaust System
The primary purpose of the exhaust system is to remove the harmful gases produced during combustion, such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons.
These gases can be dangerous to both the environment and your health if not properly expelled.
Additionally, the exhaust system helps to reduce engine noise and improve fuel efficiency.
Main Components
The exhaust system is made up of several components, including the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe.
The exhaust manifold collects the gases produced by the engine’s cylinders and directs them towards the catalytic converter.
The catalytic converter then converts these harmful gases into less harmful ones before they are released into the atmosphere.
The muffler helps to reduce engine noise by absorbing sound waves, and the tailpipe directs the exhaust gases away from the vehicle.
Flow of Exhaust Gases
The flow of exhaust gases through the exhaust system is a crucial factor in its overall performance.
The exhaust gases are expelled from the engine’s cylinders and enter the exhaust manifold, where they are collected and directed towards the catalytic converter.
The catalytic converter converts the harmful gases into less harmful ones before they pass through the muffler and out of the tailpipe.
Understanding the basics of the exhaust system and its components is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and ensuring the safe and efficient removal of harmful gases.
By regularly inspecting and replacing worn or damaged components, you can help to prolong the life of your exhaust system and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
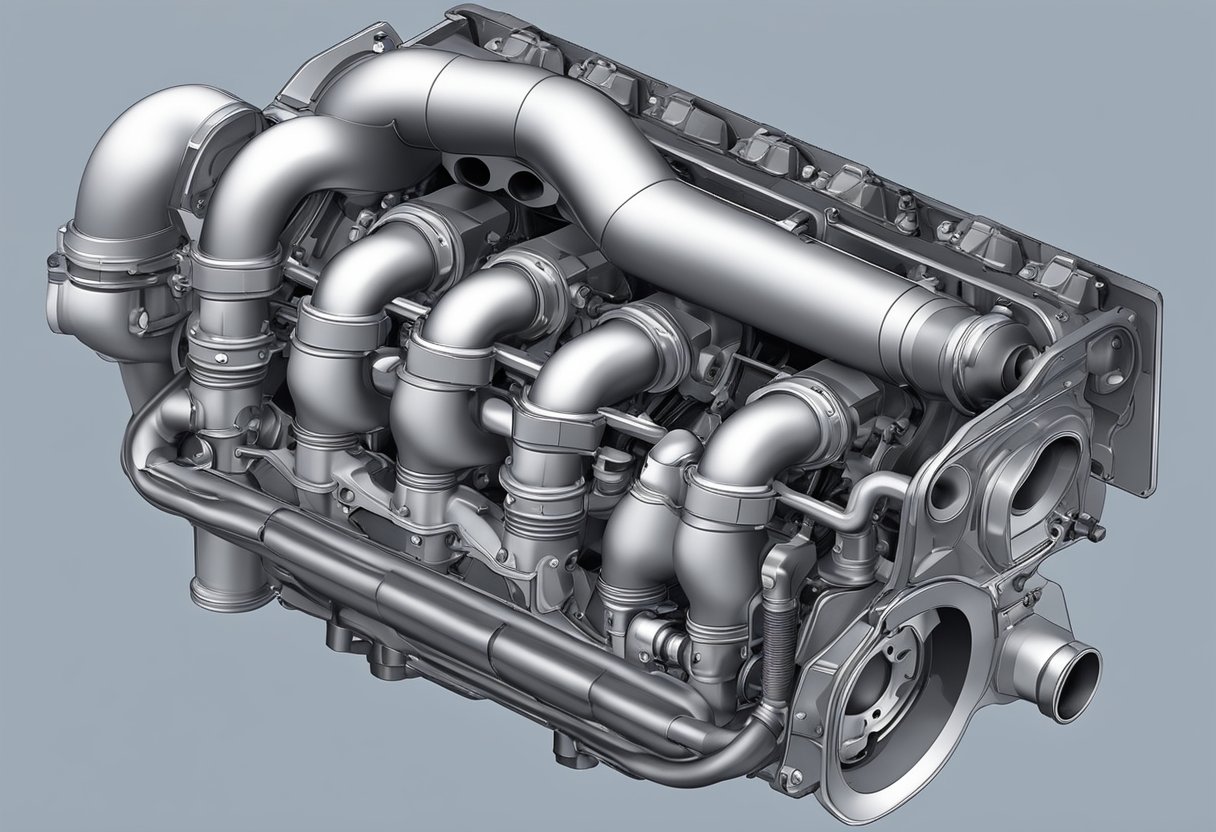
Exhaust Manifold
Function of the Manifold
The exhaust manifold is a crucial component of the exhaust system, responsible for collecting exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders and directing them into the exhaust pipes.
The manifold is typically located at the engine’s head and is bolted directly onto it.
The primary function of the manifold is to channel the exhaust gases away from the engine and reduce back pressure, which can improve engine performance.
Materials and Design
Exhaust manifolds are typically made of cast iron, stainless steel, or mild steel.
Stainless steel manifolds are more expensive but offer better durability and corrosion resistance.
Mild steel manifolds are the most affordable but are more prone to rusting.
Cast iron manifolds are durable and offer good heat retention, but they are heavy and can crack under extreme temperatures.
The design of the manifold can also affect engine performance.
The shape and size of the manifold’s runners, which are the tubes that connect the engine’s cylinders to the collector, can impact the engine’s power and torque.
A well-designed manifold can improve engine performance by increasing exhaust flow and reducing back pressure.
In summary, the exhaust manifold plays a critical role in the exhaust system by channeling exhaust gases away from the engine and reducing back pressure.
The material and design of the manifold can impact engine performance, making it important to choose the right type of manifold for your vehicle.
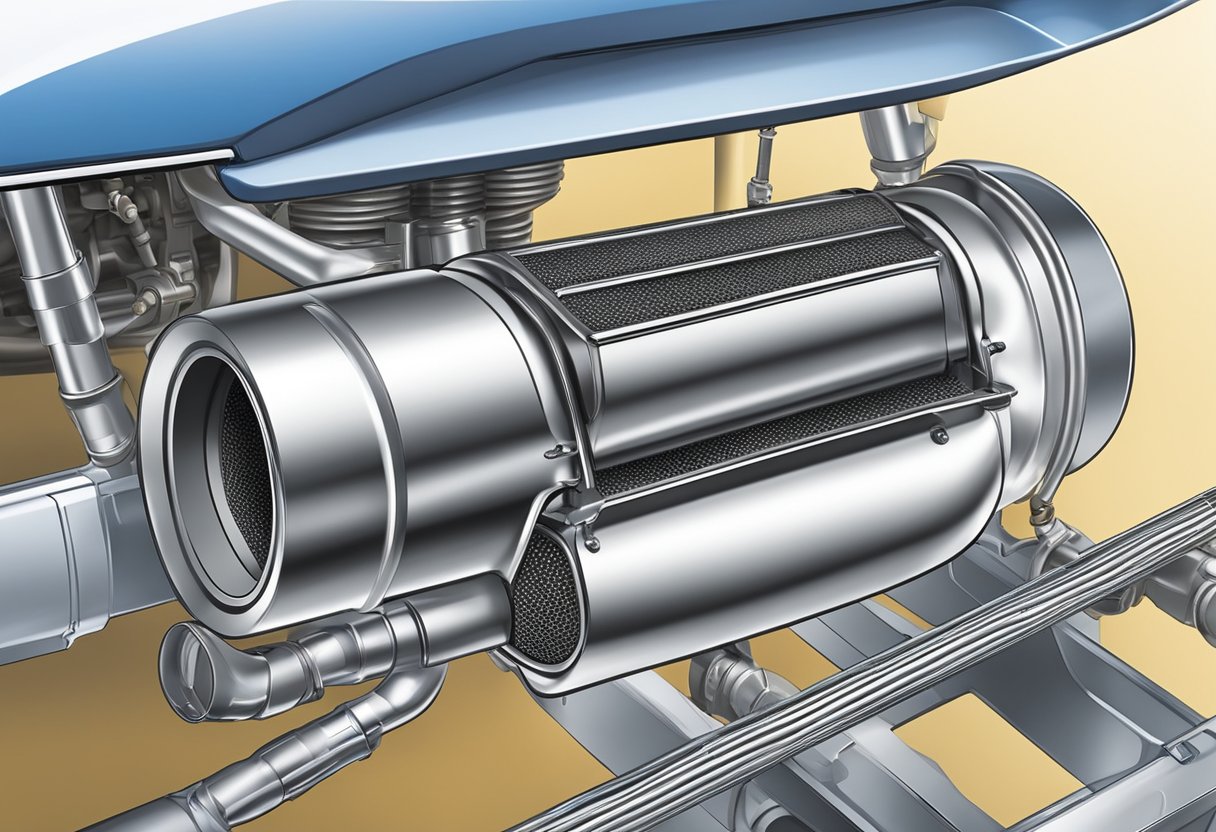
Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter is an essential component of your vehicle’s exhaust system.
It helps to reduce harmful emissions that can damage the environment and cause health problems.
Understanding the parts and functions of a catalytic converter can help you maintain your vehicle’s exhaust system and ensure it is operating efficiently.
Emission Control
The primary function of a catalytic converter is to reduce the amount of harmful emissions that are released into the environment.
It does this by converting toxic gases such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrogen gas.
Catalyst Materials
Catalytic converters contain a catalyst material, which is typically made up of precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium.
These metals are used because they are excellent at catalyzing chemical reactions.
The catalyst material is coated onto a ceramic or metallic substrate, which provides a large surface area for the chemical reactions to occur.
Converter Types
There are two main types of catalytic converters: two-way and three-way.
Two-way catalytic converters are used on older vehicles and only reduce carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon emissions.
Three-way catalytic converters are used on newer vehicles and also reduce nitrogen oxide emissions.
In summary, a catalytic converter is a crucial component of your vehicle’s exhaust system that helps to reduce harmful emissions.
It contains a catalyst material that converts toxic gases into less harmful substances.
There are two main types of catalytic converters, and understanding their functions can help you maintain your vehicle’s exhaust system.
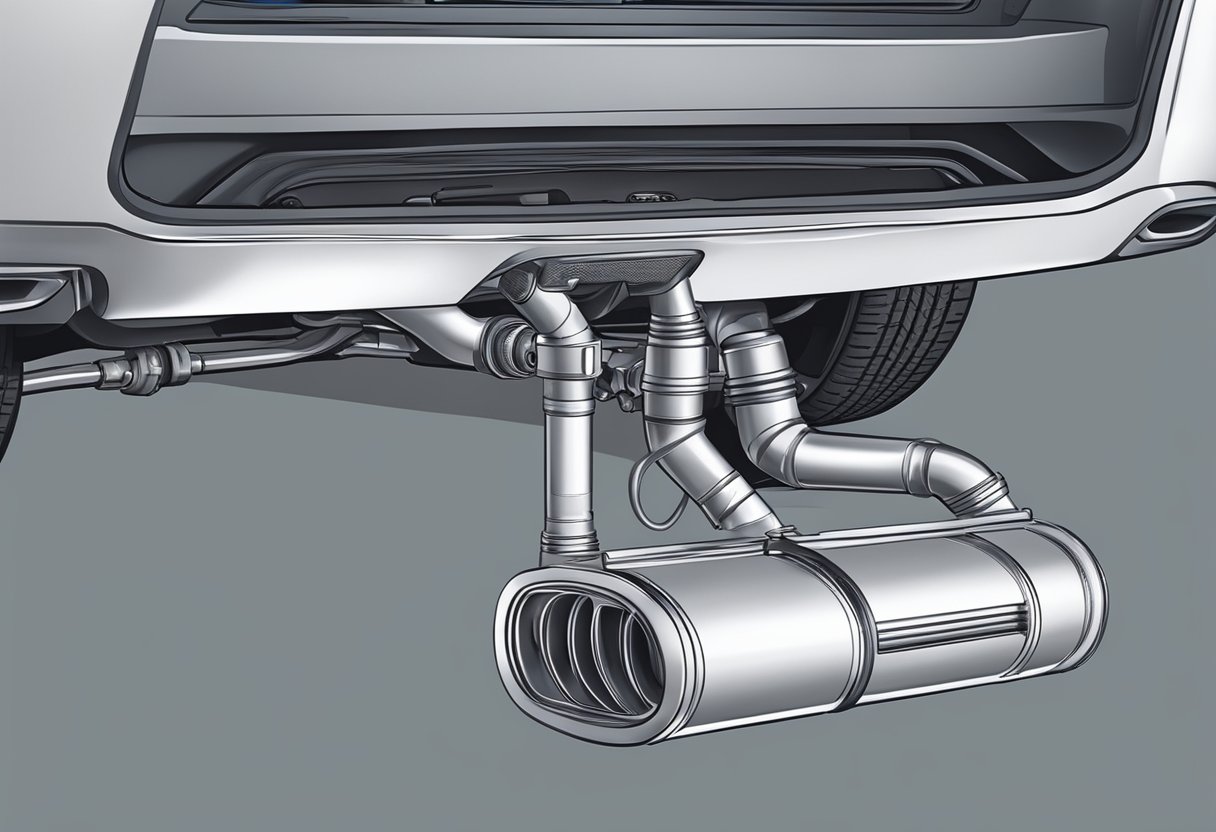
Muffler
A muffler is an essential part of your vehicle’s exhaust system that helps to reduce noise levels and improve overall engine performance.
Here are some key things you need to know about mufflers:
Noise Reduction
The primary function of a muffler is to reduce the amount of noise produced by the engine.
The muffler achieves this by using sound-absorbing materials, such as fiberglass or steel wool, to dampen the sound waves created by the engine.
As the exhaust gases pass through the muffler, they are forced to travel through a series of chambers, which further reduces the noise levels.
Muffler Design
Mufflers come in various shapes and sizes, and their design can have a significant impact on their performance.
One of the most common designs is the chambered muffler, which uses a series of chambers to reduce noise levels.
Another popular design is the straight-through muffler, which uses a perforated tube surrounded by sound-absorbing materials to reduce noise.
Performance Mufflers
In addition to reducing noise levels, some mufflers are designed to improve engine performance.
Performance mufflers are typically less restrictive than standard mufflers, allowing for better exhaust flow and increased horsepower.
However, it’s important to note that not all performance mufflers are created equal, and some may produce excessive noise levels or cause other issues if not installed correctly.
Overall, the muffler plays a crucial role in your vehicle’s exhaust system, helping to reduce noise levels and improve engine performance.
By understanding the different types of mufflers available and their functions, you can make an informed decision when selecting a muffler for your vehicle.
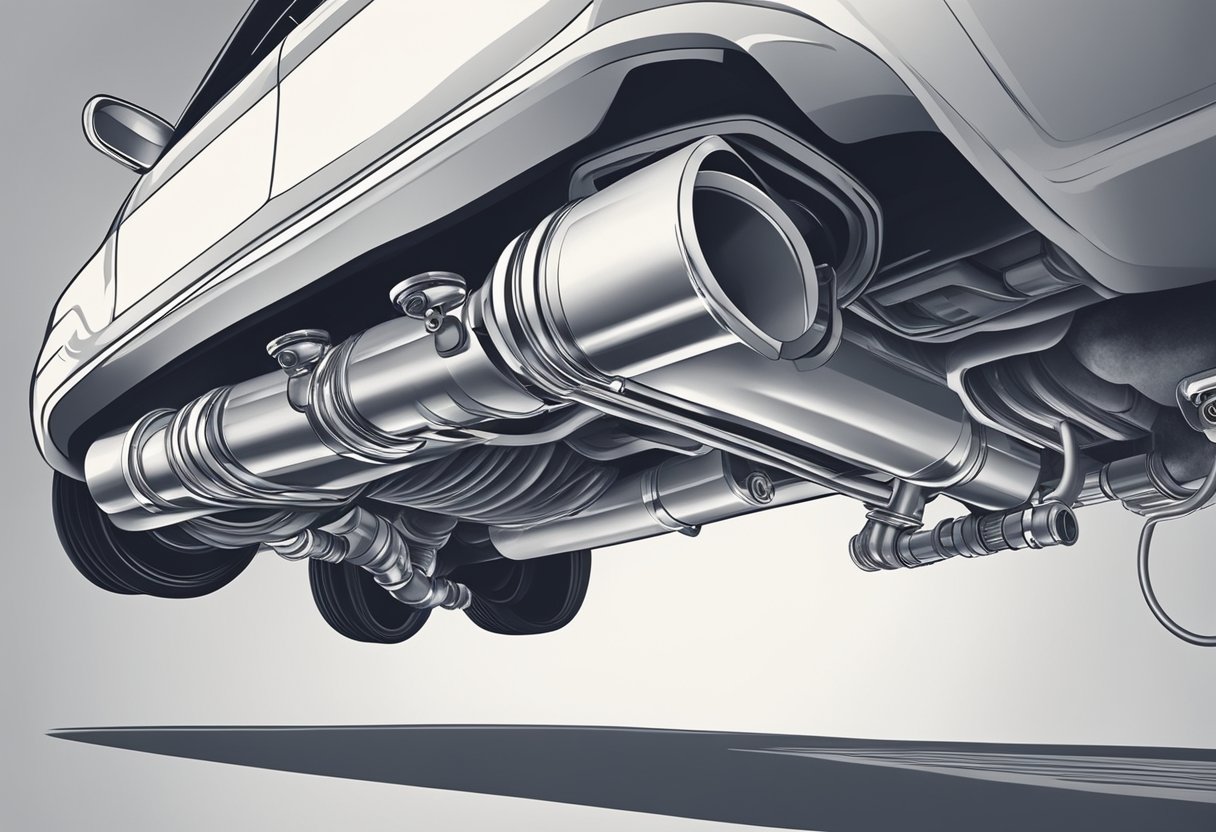
Exhaust Pipes and Tailpipe
Pipe Materials
Exhaust pipes are made from a variety of materials. The most common types of materials used for exhaust pipes are:
- Stainless steel: This is the most expensive material, but it is the most durable and resistant to corrosion.
- Aluminized steel: This is a cheaper alternative to stainless steel. It is also durable and resistant to corrosion.
- Mild steel: This is the cheapest material used for exhaust pipes.
It is not as durable as stainless steel or aluminized steel and it is prone to rust.
Exhaust Pipe Design
The design of the exhaust pipe is important because it affects the performance of the engine.
The exhaust pipe must be designed to allow the exhaust gases to flow out of the engine quickly and efficiently.
The following are some common exhaust pipe designs:
- Straight pipe: This is the simplest design. It is a straight pipe that runs from the engine to the tailpipe.
- Header: This design is used in high-performance engines. It has a series of pipes that merge into one larger pipe.
- Dual exhaust: This design has two exhaust pipes that run from the engine to the tailpipe.
Tailpipe Function
The tailpipe is the final part of the exhaust system.
Its function is to release the exhaust gases from the engine into the atmosphere.
The tailpipe must be designed to reduce the noise from the engine and to prevent harmful gases from entering the cabin of the vehicle.
The following are some common tailpipe designs:
- Straight cut: This is the simplest design. It is a straight pipe that runs from the exhaust system to the back of the vehicle.
- Rolled edge: This design has a rolled edge at the end of the tailpipe.
It is a popular design because it looks more stylish than a straight cut tailpipe.
- Turn down: This design has a pipe that is turned down at the end. It is used to direct the exhaust gases away from the ground.
Understanding the different parts of the exhaust system and how they function is important for maintaining the performance of your vehicle.
By knowing the materials used for exhaust pipes, the different designs of exhaust pipes, and the function of the tailpipe, you can make informed decisions when it comes to upgrading or repairing your exhaust system.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.